Summary and comparison of the imaging quality of IOLs
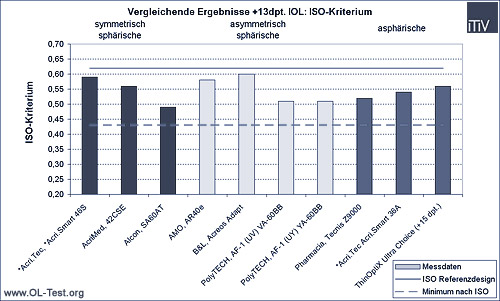
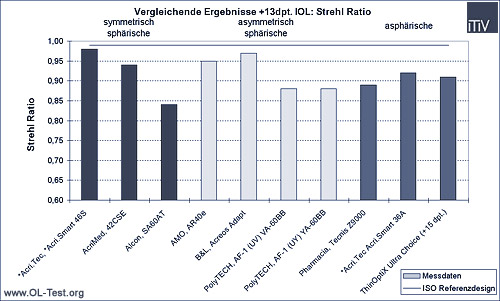
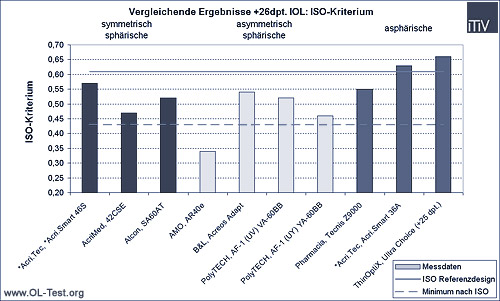
The following graphs show the comparison of the different IOLs tested according to the three basic design types: symmetrical spherical, asymmetrical spherical and aspherical. The measurement results of the Strehl ratio (comparison of the tested lens to the diffraction-limited ideal lens) and the ISO criterion (modulation of the MTF at a spatial frequency of 100 line pairs/mm) are shown in each case. For the latter, the result of the ideal symmetrically spherical ISO reference design (upper solid line) and the minimum value required by ISO for a symmetrically spherical design (lower solid line) are also shown.
The detailed measurement data is organized according to the following design types:
List of the IOLs examined:
| Manufacturer | IOL type | Design Type | Refractive power |
| *Acri.Tec | *Acri.Smart 46S | sym. spherical | +13dpt., +26dpt. |
| *Acri.Tec | *Acri.Smart 36A | aspheric | +13dpt., +26dpt. |
| AcriMed | 42CSE | sym. spherical | +13dpt., +26dpt. |
| Alcon | SA60AT | sym. spherical | +13dpt., +26dpt. |
| AMO | AR40e | asym. spherical | +13dpt., +26dpt. |
| Bausch & Lomb | Akreos Adapt | asym. spherical | +13dpt., +26dpt. |
| Pharmacia | Tecnis Z9000 | aspheric | +13dpt., +26dpt. |
| PolyTECH (HOYA) | AF-1 (UV) VA-60BB | asym. spherical | +13dpt., +26dpt. |
| PolyTECH (HOYA) | AF-1 (UY) YA-60BB, Blue Blocker | asym. spherical, yellow | +13dpt., +26dpt. |
| Sifi | Mini 4 | aspherical | +13dpt., +26 dpt. |
| ThinOptiX | Ultra Choice PHC001 | aspherical | +15dpt., +25dpt. |
Summary of the measurement results in comparison
IOL with a refractive power of +13dpt:
IOL with a refractive power of +26dpt:
Discussion
As can be seen from the above comparison of the measurement results, there are in some cases considerable differences in the image quality of current IOLs. As expected due to the dominant spherical aberration, these differences are particularly evident at higher refractive powers. Design and manufacturing errors are particularly noticeable here. These can be fully compensated for by aspheric designs.
The Strehl Ratio (SR) can be used to compare different refractive powers, as this is independent of the refractive power compared to the ISO criterion. While the SR of symmetrical and asymmetrical spherical designs drops significantly at +26dpt. compared to +13dpt., this value remains almost the same for aspherical IOLs. In comparison to highly refractive and spherical designs (modulations between 0.62 and 0.66, SR 0.75 to 0.85), aspheric IOLs (modulations from 0.62 to 0.66, SR from 0.91 to 0.97) achieve an improvement in image quality of up to 1.40 times.
The sometimes significant deviation of the measured values of aspheric IOLs from the ideal value of 1.00 can essentially be explained by the aspheric cornea model [Brennan97] on which the design is based (so-called 'aberration-corrected' IOLs: *Acri.Smart 36A and Ultra Chice PHC001). Since the artificial eye according to ISO [ISO11979] is based on a spherical cornea model, this inevitably leads to a slight deterioration in the measured values according to ISO. However, if one compares the curvature of the curves of the two different refractive powers in these IOLs, they are almost identical and therefore there is no recognizable spherical aberration. The significantly different curvatures of the MTF curve when comparing the different designs of different manufacturers, on the other hand, suggest that different corneal models (asphericities) are the basis.
All lenses measured (apart from the AMO AR40e +26dpt.) meet the ISO requirements (which are based on a symmetrical spherical design). However, the image qualities are clearly different. In the case of the +13dpt. IOL, the image quality varies by 18% according to the ISO criterion (14% according to SR), in the case of the +26dpt. IOL by 49% according to ISO (29% according to SR). Well-designed aspheric IOLs therefore offer significantly better image quality compared to spherical IOLs, especially for large refractive powers of +26dpt.
Contact
Prof. Dr. rer.nat. Wilhelm Stork
Tel. 0721 / 608 - 42510, wilhelm.stork∂kit.edu

